Color Theory in Graphic Design
Colour theory is a crucial aspect of graphic design. It influences how designs are perceived. Designers use colour to evoke emotions and convey messages. Understanding colour theory helps create effective visuals. This guide explores the basics of colour theory and its application in graphic design.
The Color Wheel
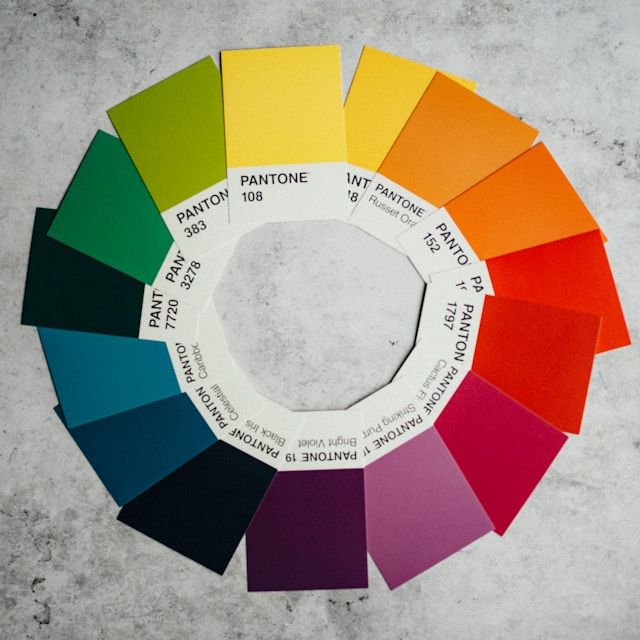
The colour wheel is a visual representation of colours. It consists of primary, secondary, and tertiary colours. The primary colours are red, blue, and yellow. These colours cannot be created by mixing others. The secondary colours are green, orange, and purple. They are made by mixing primary colours. For instance, mixing blue and yellow creates green. Tertiary colours result from mixing primary and secondary colours.
Designers often use the colour wheel to select harmonious colour combinations. Complementary colours are opposite each other on the wheel. For example, blue and orange create a strong contrast. This contrast makes designs vibrant. In contrast, analogous colours sit next to each other. For instance, blue, blue-green, and green create a calm, cohesive look.

Color Harmony
Colour harmony is essential in graphic design. It refers to the arrangement of colours that work well together. Designers use colour schemes to achieve harmony. Common schemes include monochromatic, analogous, and complementary.
Monochromatic schemes use different shades and tints of a single colour. This creates a unified and sophisticated look. For example, light blue, medium blue, and dark blue can evoke feelings of calmness and trust. On the other hand, analogous schemes combine colours that are next to each other on the colour wheel see fronlinecasino.lv . This approach creates a smooth transition between colours.
Complementary schemes use colours that are opposite each other. This scheme creates dynamic visuals. The contrast between colours grabs attention. For instance, a design using blue and orange will stand out.


Colour Psychology
Colour has a significant impact on emotions and perceptions. This is known as colour psychology. Different colours evoke different feelings. Understanding this can enhance a design's effectiveness.
For example, red often signifies passion and energy. It can stimulate excitement and urgency. This is why it is commonly used in sales and promotions. In contrast, blue conveys calmness and trust. It is often used by banks and healthcare brands.
Green represents nature and growth. It is a popular choice for eco-friendly brands. Yellow exudes happiness and positivity. It can attract attention but should be used sparingly to avoid overwhelming the viewer. Understanding these associations helps designers choose colours that align with the message they want to convey.
The Importance of Contrast
Contrast is another critical element in graphic design. It refers to the difference between colours, which can enhance readability and draw attention. High contrast makes the text stand out against the background. This ensures that the message is clear.
For instance, black text on a white background is highly readable. However, low contrast, such as light grey text on a white background, can be difficult to read. Designers should consider contrast when choosing colour combinations. It is essential for accessibility as well. High contrast ensures that designs are legible for all viewers, including those with visual impairments.
Cultural Significance of Colors
Colours carry different meanings across cultures. Designers must consider the cultural context when selecting colours. For instance, white symbolizes purity in many Western cultures. However, it represents mourning in some Eastern cultures. Similarly, red can signify good fortune in Chinese culture but may represent danger in Western contexts.
Therefore, understanding cultural significance is vital for global brands. It helps avoid misunderstandings and ensures that the message is conveyed correctly. Designers should conduct research on cultural meanings when working on international projects.
Using Color in Branding
Colour plays a crucial role in branding. It helps establish brand identity and recognition. Consistent use of colour across all marketing materials creates a cohesive brand image. For example, the colour blue is often associated with trust and reliability. Brands like Facebook and Twitter use blue to convey these traits.
Moreover, colours can differentiate a brand from its competitors. In a crowded market, unique colour choices help brands stand out. Designers should carefully select colours that align with the brand's values and target audience.
Tools for Color Selection
Designers have various tools at their disposal for colour selection. Online colour pickers and generators can help identify harmonious colour schemes. Adobe Color and Coolors are popular options. These tools allow designers to experiment with different colour combinations easily.
Additionally, designers can use Pantone colour guides. Pantone provides standardized colours that ensure consistency in printing and production. Using these tools helps streamline the design process and ensures colour accuracy.
Conclusion
Color theory is fundamental in graphic design. It influences how designs are perceived and interpreted. Understanding the colour wheel, colour harmony, and colour psychology is essential for creating effective visuals. Designers must also consider contrast, cultural significance, and branding when selecting colours.